What Is EPDM Roofing? Pros, Cons, and Where It’s Used
If you own or manage a building with a flat or low-slope roof, you may have heard about EPDM roofing. It’s one of the most common roofing systems used on commercial buildings across the United States.
So the big question is:
What is EPDM roofing, and is it a good choice?
This guide explains EPDM roofing in a clear and simple way, so you understand what it is, how it works, how long it lasts, and when it makes sense to use it.

What Does EPDM Stand For in Roofing?
EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, but you don’t need to remember that. What matters is how it behaves on a roof.
That name sounds technical, but the idea is simple.
EPDM roofing is a synthetic rubber membrane. In real life, it looks like a large black rubber sheet that’s rolled out over flat or low-slope roofs in wide sections. Because it comes in large sheets, it reduces the number of seams — which is one of the most important factors in preventing leaks on flat roofs.
EPDM is commonly used on:
-
Commercial buildings
-
Warehouses
-
Office buildings
-
Apartment complexes
-
Some flat residential roofs
What Is EPDM Roofing Made Of?
EPDM is made from synthetic rubber, and that material choice is not accidental.
Rubber allows EPDM roofs to stay flexible in extreme temperatures. Instead of becoming brittle in cold weather or cracking under intense sun, the material expands and contracts naturally as temperatures change. This flexibility is one of the reasons EPDM has been trusted for decades.
From what we see in the field, roofs that can move slightly with temperature changes tend to age more evenly than rigid systems that fight those movements.
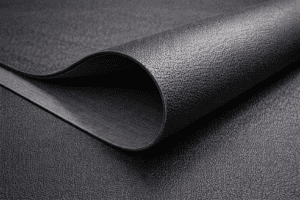
How Is EPDM Roofing Installed?
Before installing or replacing an EPDM roof, a professional roof inspection helps identify existing issues and determine the best solution.
Flat roofs often hide problems below the surface, and skipping this step can lead to installing new material over existing issues.
Once the roof is ready, EPDM is installed in large sheets using one of several methods. Some systems are fully adhered with adhesive, others are mechanically fastened, and some are ballasted with stone to hold the membrane in place. Regardless of the method, the most important part of the installation is how the seams are handled.
Unlike systems that use heat-welded seams, EPDM seams rely on specialized adhesives or seam tape. When done correctly, these seams are reliable and watertight. When done poorly, they become the first point of failure. That’s why EPDM installation is not a DIY project and should always be handled by experienced professionals.
Why Is EPDM Roofing So Popular?
EPDM has been used for decades, and there are good reasons it’s still popular today.
Proven Durability
One major reason is durability. Many EPDM roofs last 25 to 30 years — and sometimes longer — when installed properly and maintained over time.
Weather Resistance
The material also performs well in a wide range of weather conditions, handling rain, wind, heat, and temperature swings without major issues. The rubber material handles:
-
Heat
-
Cold
-
Rain
-
Wind
Cost-Effective
Another reason is cost. Compared to some newer flat roofing systems, EPDM is often more affordable upfront while still offering reliable long-term performance. It also tends to require less maintenance than more complex roofing systems.
Low Maintenance
EPDM roofs usually require minimal maintenance compared to more complex systems.

How Long Does EPDM Roofing Last?
On average, EPDM roofing lasts 25 to 30 years, but lifespan isn’t determined by material alone.
Regular inspections play a major role in extending roof lifespan and preventing small problems from becoming expensive repairs.
Lifespan depends on:
-
Installation quality
-
Climate
-
Maintenance
-
Foot traffic
If you want to understand how EPDM compares to other roofing systems over time, this guide explains roof lifespan in more detail:
How Long Does a Roof Last?
EPDM Roofing vs TPO Roofing
EPDM is often compared to TPO roofing because both are commonly used on flat roofs, but they behave differently.
EPDM is usually black, which means it absorbs heat. It’s extremely flexible and has a long, proven track record. TPO, on the other hand, is typically white, reflects sunlight, and is often chosen for its energy efficiency. TPO seams are heat-welded rather than glued.
EPDM Roofing
-
Usually black
-
Absorbs heat
-
Extremely flexible
-
Long history
TPO Roofing
-
Usually white
-
Reflects sunlight
-
More energy efficient
-
Heat-welded seams
Neither system is automatically better. The right choice depends on the building design, insulation, energy goals, and local climate. If you want a deeper breakdown of the differences, this guide explains TPO clearly:
What Is TPO Roofing?
👉 The better option depends on the building, climate, and energy goals.

Is EPDM Roofing Good for Florida?
EPDM can work well in Florida, but there are trade-offs.
The material handles heavy rain and weather changes very well, which is important in storm-prone areas. However, because EPDM is black, it absorbs heat. In Florida’s climate, that can increase cooling demands if the building isn’t well insulated.
Pros in Florida
-
Handles heavy rain well
-
Flexible during temperature changes
-
Proven durability
Cons in Florida
-
Black surface absorbs heat
-
Can increase cooling costs
For that reason, EPDM is often used on commercial buildings where insulation and roof design help manage heat effectively.
For many Florida properties, EPDM and TPO are both solid options for commercial roofing
What Are the Disadvantages of EPDM Roofing?
No roofing system is perfect.
Possible downsides include:
-
Seams rely on adhesive instead of welding
-
Black color absorbs heat
-
Punctures possible from sharp objects
The good news is that most of these risks are manageable with proper installation, routine inspections, and timely repairs.
Why Professional Installation Matters for EPDM Roofing
EPDM roofing is not a DIY system.
EPDM roofing rewards good workmanship and punishes poor workmanship.
Improper installation can lead to seam failures, leaks, and a much shorter lifespan.
That’s why working with experienced commercial roofers is critical. A well-installed EPDM roof can perform reliably for decades, while a poorly installed one can fail much sooner.

EPDM Roofing and Roof Replacement
EPDM roofing is commonly installed during full roof replacement projects on flat roofs.
Flat roof replacement costs can vary based on size, materials, and installation method.
A professional inspection helps determine whether a roof needs replacement or repairs.
Why Choose JA Edwards of America for EPDM Roofing?
At JA Edwards of America, we’ve worked with EPDM roofing systems across Florida and understand how local weather impacts flat roofs.
Our team focuses on:
-
Proper installation
-
Quality materials
-
Long-term performance
We help property owners understand the pros and cons of each roofing option before making a decision.
FAQ: What Is EPDM Roofing?
What is EPDM roofing used for?
EPDM roofing is mainly used on flat or low-slope commercial roofs.
Is EPDM roofing waterproof?
Yes. When installed correctly, EPDM provides strong waterproof protection.
Is EPDM roofing better than TPO?
Neither is always better. EPDM absorbs heat, while TPO reflects it. The best choice depends on the building and climate.
Can EPDM roofing be repaired?
Yes. Small tears or seam issues can often be repaired if caught early.
Does EPDM roofing require maintenance?
Minimal maintenance is required, but regular inspections are recommended.
Final Thoughts
So, what is EPDM roofing?
It’s a durable, flexible rubber roofing system designed for flat and low-slope roofs, especially on commercial buildings. When installed correctly and maintained over time, EPDM offers long-term protection at a reasonable cost.
If you’re considering EPDM or comparing flat roofing options, starting with a professional inspection is always the smartest first step.

